In today’s evolving IT landscape, organizations face escalating complexities and growing risks. Business owners must prioritize regular IT audits to safeguard their systems and ensure cybersecurity readiness. These audits ensure system integrity and verify optimal cost-efficiency, speed, and protocol adherence.
This blog delves into the essential steps for conducting a successful IT audit, empowering businesses to manage IT risks proactively.
Table of Content
What is an IT Audit?
Different Variants of IT Audit
Why does your organization need an IT Audit?
Let’s dive deep: Steps to conduct a successful IT Audit
Potential Challenges of IT Audit
Personalized assurance for your IT infrastructure
Initiate your journey with an IT security companion
FAQs
What Is An IT Audit?
In general, the meaning of audit involves examining an existing system, report, or entity as part of an investigative process.
An IT audit is a comprehensive evaluation of an organization’s information technology infrastructure, policies, and procedures. Its purpose is to ensure the seamless and secure functioning of IT systems while empowering employees to utilize them safely and effectively.
Picture an IT security audit, as an examination that tests the effectiveness of the company’s protective measures. It verifies if IT controls are safeguarding valuable assets, preserving data integrity, and aligning with the company’s goals. From physical security to financial concerns, every aspect of the IT realm undergoes meticulous consideration.
Different Variants Of IT Audit
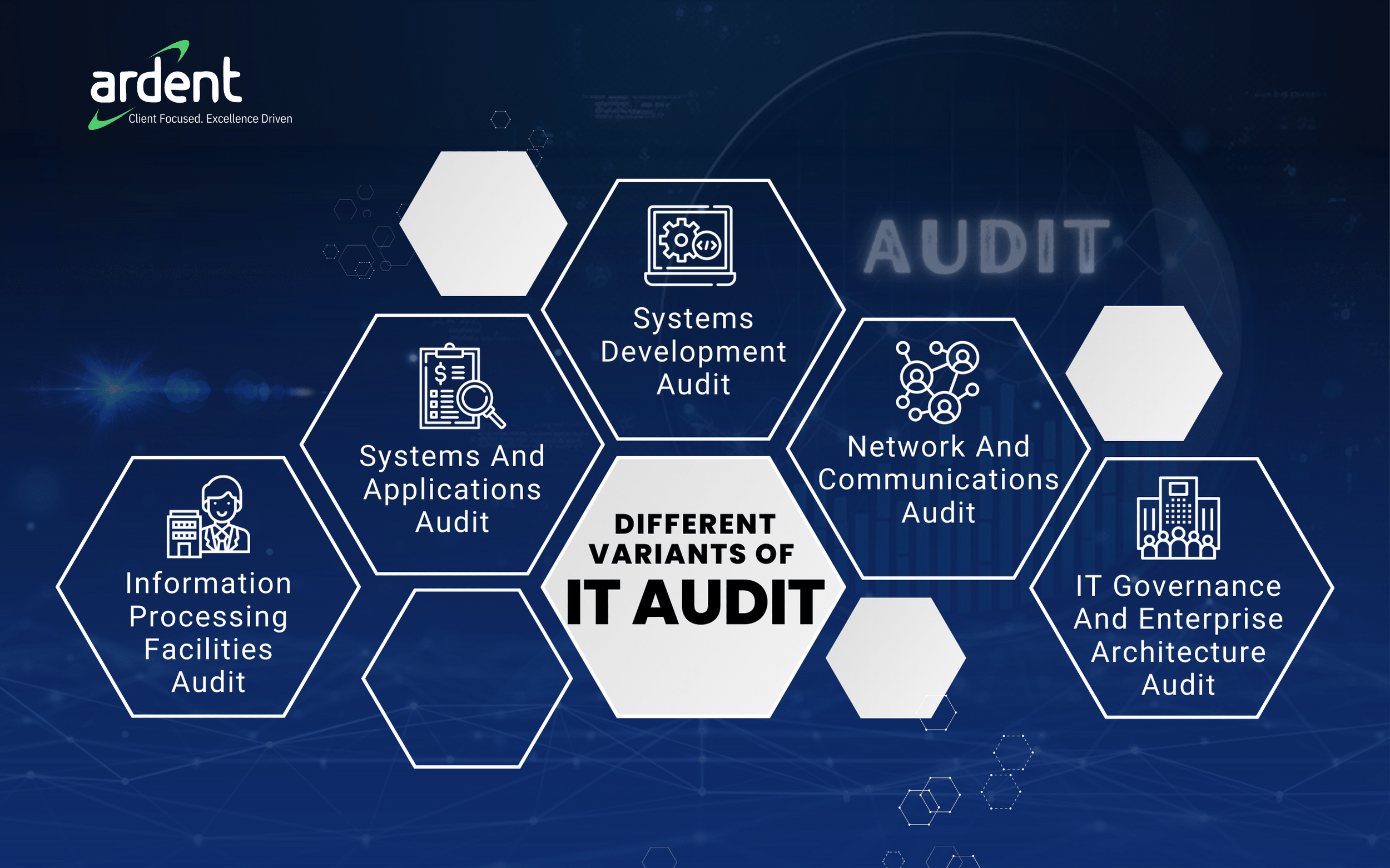
Why Does Your Organization Need An IT Audit?
- Identify Risks: IT audits help identify potential risks and vulnerabilities in an organization’s IT systems, infrastructure, and processes. By assessing these risks, organizations can take proactive measures to mitigate them and enhance overall security.
- Ensure Compliance: IT audits ensure that organizations comply with relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards. By reviewing these, they help identify any gaps or non-compliance issues, allowing organizations to take appropriate corrective actions.
- Enhance Security: IT audits assess the effectiveness of security measures and controls in place to protect sensitive data and systems. They help identify areas where security can be strengthened and recommend improvements to safeguard against potential threats and breaches.
- Optimize IT Operations: IT audits help organizations assess the efficiency and effectiveness of their IT operations. By evaluating processes, controls, and system performance, audits can identify areas for improvement and optimize resource allocation.
- Ensure Data Integrity: IT audits verify the accuracy, completeness, and reliability of data processed by IT systems. By reviewing data management processes, audits help ensure the integrity and availability of critical information.
Steps To Conduct A Successful IT Audit
Define Scope Of Audit
In order to define scope, it is important to consult key stakeholders, including IT management, department heads, and compliance officers, to understand the organization’s unique needs, risks, and priorities. Involving stakeholders from the beginning ensures valuable insights and alignment with strategic objectives.
The scope of the audit should clearly define the boundaries of what will be covered and what will not be included. This helps prevent requirement creep. Considerations for determining the scope may include the size and complexity of the IT environment, critical systems and applications, regulatory requirements, and any specific concerns or priorities identified during the initial scoping phase.
Plan Strategically
During the “gathering information” phase, the IT auditor identifies some critical items: such as knowledge of the business and industry, prior audit results, regulatory statutes, and inherent risk assessments.
Moving on to “gaining an understanding of the existing internal control structure,” the IT auditor focuses on five additional areas and items: control environment, control procedures, detection risk assessment, control risk assessment, and equating total risk.
Once the IT auditor has gathered information and comprehended the control structure, they are prepared to begin the planning phase by selecting the areas to be audited. It’s important to have a current business impact analysis during the initial steps to help determine which applications support the most critical or sensitive business functions.
There are a lot of approaches, but many organizations nowadays adopt a risk-based audit approach, which helps IT auditors assess risk.
Conduct The Audit
General controls are broad and encompass all areas of the organization, including IT infrastructure and support services. They cover various aspects such as internal accounting controls, operational controls, administrative controls, security policies, and procedures. These controls ensure the organization maintains the right documentation and records, implements safeguards over access, and establishes physical and logical security measures for data centers and IT resources.
On the other hand, application controls are specific to each computer-based application system. They address the accuracy, completeness, and validity of transactions and data. Application controls include ensuring that only complete, accurate, and valid data is entered and updated, that processing achieves the intended task correctly, and that the processing results meet expectations. The main goal of application controls is to maintain the integrity and accuracy of records and entries.
Document Findings And Recommendations
To ensure effective communication, the following need to be assured:
Factual accuracy and evidence support.
Practical and cost-effective recommendations
Agreement on implementation dates for recommendations.
The report should include:
Executive summary: Concise overview of objectives, scope, and key findings.
Audit findings: Detailed description of issues, vulnerabilities, and areas for improvement.
Recommendations: Clear actions supported by sound reasoning.
Management’s response: Their agreement/disagreement and planned actions.
Conclusion: Summary of the overall assessment.
Communicate And Follow Up
Upon applying the recommendations from the IT audit report, organizations proceed to implement the proposed improvements. A subsequent round of testing is conducted to verify the effectiveness of the IT audit resolutions, ensuring they function as intended. Once the follow-up confirms successful implementation, the IT audit is officially concluded and marked as closed.
Potential Challenges Of IT Audit
- Audit protocols for data management and governance are becoming more challenging as organizations adopt artificial intelligence, machine learning, and real-time monitoring. These technologies introduce complex risks that need to be addressed.
- Understanding the impact of various tools and technologies on cybersecurity and privacy is becoming increasingly difficult for companies operating in the cloud. As they become more advanced, it becomes crucial to assess how these factors are affected.
- Integrating emerging technologies often require infrastructure changes, which can bring significant complexity.
- Examining third-party partners and vendors in the cloud supply chain can pose obstacles during investigations due to their own policies and protocols. It is important to address these challenges and find solutions before committing to a specific cloud vendor.
Personalized Assurance For Your IT Infrastructure
Ensures the safety of your IT systems with Ardent IT Consulting. With our expertise and experience, we offer personalized assurance by specializing in various domains to identify and mitigate potential risks and failures in your infrastructure. Contact us now to learn how we can safeguard your IT infrastructure.
Initiate Your Journey With An IT Security Companion!
Ardent IT provides a variety of services aimed at safeguarding your business from harmful attacks that can cause significant damage to your IT infrastructure.
- Compliance & Risk Management: Evaluate processes, reduce risk, and address vulnerabilities for system security and regulatory compliance.
- Network Security Management: Gain comprehensive network visibility, analyze data for specific devices, and ensure network security through policy updates.
- Security Policy Management: Identify and mitigate IT vulnerabilities, restore systems after incidents, and meet advanced threats and compliance requirements for sustained security.
- Email Security Services: Protect against unauthorized access, data loss, and compromise through content filtering, encryption, and compliance archiving.
- Malware Protection Services: Add an extra layer of defense with antivirus software, scanning for malware in downloads, regular system scans, and timely updates to stay protected against the latest threats.
Secure Your Systems Now!
FAQ’s
IT audits evaluate an organization’s IT infrastructure, policies, procedures, and documentation. This includes analyzing networks, applications, security protocols, and data management.
An IT audit should cover general controls (e.g., security policies and access controls) and application controls (e.g. data integrity and processing accuracy) to ensure a comprehensive assessment of the IT environment.
Best practices for a successful IT audit include thorough planning, clear objectives, adequate documentation, evidence gathering, independent review, and timely reporting.
To prepare for an IT audit, organizations should establish strong IT policies and procedures, maintain accurate documentation, conduct regular internal assessments, and address any identified vulnerabilities or non-compliance issues proactively

